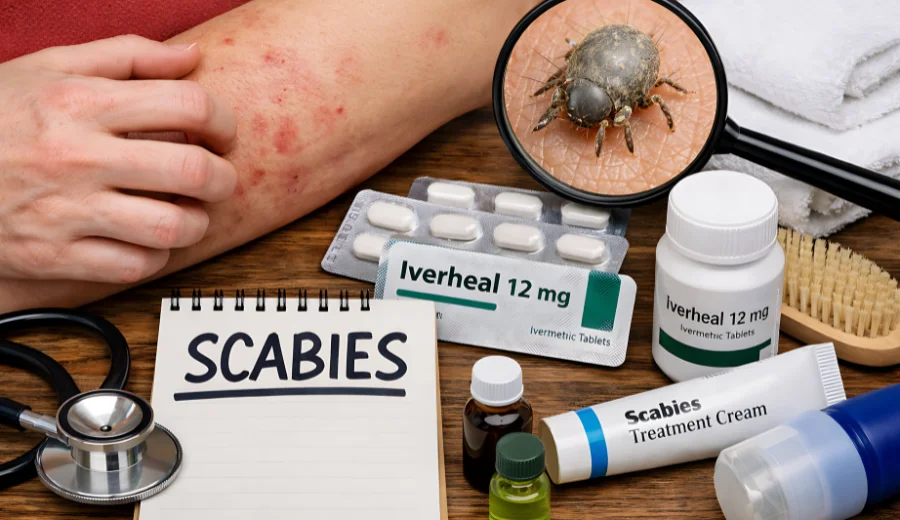
Scabies is a common skin condition that causes intense itching and skin irritation. Many people confuse it with allergies or insect bites, which often delays correct treatment.
When scabies is not treated on time, it can spread quickly from one person to another. This can lead to serious discomfort, skin damage, and ongoing itching.
This guide explains how to safely and effectively rid of scabies using medical treatment, proper care, and prevention steps.
What Is Scabies?
Scabies is a skin infection caused by very small mites that live under the skin. These mites burrow into the top layer of the skin and lay eggs there, which leads to irritation.
As the mites move under the skin, they trigger an allergic reaction. This reaction causes redness, itching, and visible skin rashes.
Scabies spreads through close skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. In some treatment plans, medicines such as iverheal 12 mg may be prescribed by a doctor, and the infection can also spread by sharing clothes, towels, or bedding, affecting people of any age.
Common Symptoms of Scabies
The symptoms of scabies usually appear a few weeks after infection. In people who have had scabies before, symptoms may develop faster.
Common signs include:
-
Severe itching, especially at night
-
Red rashes or small bumps on the skin
-
Thin lines or burrow marks
-
Sores caused by frequent scratching
-
Skin irritation between fingers, wrists, waist, or elbows
Itching may continue for some time after treatment begins, but this does not always mean the treatment has failed.
How Is Scabies Diagnosed?
Scabies is usually diagnosed by a doctor through a physical skin examination. The doctor checks the rash pattern and areas where itching is most intense.
Key Points:
-
Doctors look for typical rash patterns
-
Burrow marks on the skin are examined
-
Areas with severe itching are checked carefully
-
A skin scraping test may be done if needed
-
Self-diagnosis should be avoided
Because many skin conditions look similar, professional diagnosis is important.
How to Get Rid of Scabies – Best Treatment Options
The most effective way to treat scabies is through prescribed medical treatment. Home remedies alone cannot fully remove scabies mites.
Topical Treatment
Doctors often prescribe medicated creams or lotions that are applied to the entire body from the neck down. These medicines kill the mites present on the skin.
The cream must stay on the skin for the recommended time before being washed off. In some cases, a second application is advised to ensure complete treatment.
Oral Medicines
In moderate to severe cases, oral medicines may be prescribed when topical treatment does not work well. One such option is iverheal 6mg, which is used under strict medical guidance.
These medicines work from inside the body to help control the infection. They should never be taken without a doctor’s advice.
Alternative Oral Option
In some situations, ivermectin 3mg tablets may be recommended by a healthcare professional. This option is generally used when scabies does not respond to standard treatment.
These tablets help eliminate mites internally and must be taken exactly as prescribed.
Supportive Care
Treatment also focuses on scabies itching relief. Doctors may suggest antihistamines or soothing lotions to reduce itching and help the skin heal.
Along with prescribed treatment, a balanced diet that includes nutrients such as Omega-3 may help support overall skin health during recovery.
Can Scabies Come Back?
Yes, scabies can return if treatment is not completed properly. One common reason is that close contacts were not treated at the same time, even if they do not show symptoms.
Even if only one person shows symptoms, all household members should receive treatment together. Medicines such as Ivermectin for humans are sometimes discussed for parasite-related infections, but treatment must always follow medical advice.
Completing the full course of scabies treatment is essential to avoid the infection coming back and to prevent reinfection within the household.
Prevention Tips for Scabies
Preventing scabies is possible by following simple precautions during and after treatment.
-
Wash clothes, towels, and bedding in hot water
-
Dry items using high heat
-
Avoid sharing personal items
-
Limit close skin contact until treatment is complete
-
Follow medical instructions carefully
Good hygiene and proper cleaning play a major role in preventing reinfection.
FAQs
Q1. What causes scabies?
Scabies is caused by tiny mites that live under the skin and trigger itching and rashes.
Q2. How does scabies spread?
Scabies spreads through close skin-to-skin contact or by sharing clothes, towels, or bedding.
Q3. How long does scabies take to heal?
With proper treatment, scabies usually improves within a few weeks, though itching may last longer.
Q4. Can scabies go away without treatment?
No, scabies does not go away on its own and requires medical treatment to remove the mites.
Q5. Can scabies come back after treatment?
Yes, scabies can return if treatment is not completed or close contacts are not treated together.
Conclusion
Scabies is uncomfortable but completely treatable with the right medical care. Early diagnosis and proper medication help control the infection and reduce itching.
Good hygiene plays an important role during treatment and recovery. While some people read about medicines such as Hydroxychloroquine, scabies treatment should always follow doctor-recommended options specific to this condition.
Always complete the prescribed treatment and make sure close contacts are treated as well. With the right approach, scabies can be cleared safely and effectively.